Electronic Effects
Electronic Effects: Overview
In this topic, we will understand the concept of electronic effect that occurs while electron withdrawing or electron donating group in detail. We will also discuss the polarisation of various bonds based on the polarity in adjacent bonds.
Important Questions on Electronic Effects
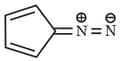
The most stable canonical structure of this molecule is:
In which of the following molecules / ions resonance structures are equivalent:
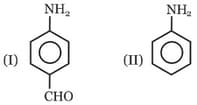
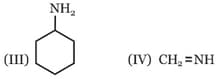
Among these compounds, the correct order of C–N bond length is :
In which of the following pairs, is the first species is more stable than second?
In which of the following molecules π-electron density in ring is maximum ?
In which of the following molecules π-electron density in ring is minimum ?
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
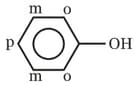
In phenol, π - electron - density is maximum on
The order of stability of these canonical forms is:
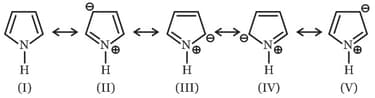
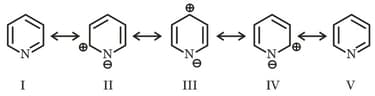
Among these canonical structures of pyridine, the correct order of stability is
The most stable resonating structure of following compound is
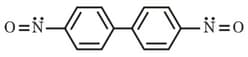
Among these three canonical structures (through more are possible) what would be their relative contribution in the hybrid?
Among these canonical structures which one is least stable ?
In which of the following molecules - group is not coplanar with phenyl ring?
In which of the following molecules resonance takes place through out the entire system
Hyperconjugation involves overlap of the following orbitals
Among the following, the least stable resonance structure is
For 1–methoxy–1,3–butadiene, which of the following resonating structure is the least stable?
What is conjugation in chemistry?
